Embolization Procedure - What You Need to Know
embolization FAQ
What is embolization & how does it work?
Embolization involves the selective occlusion of blood vessels by purposely introducing emboli, in other words deliberately blocking a blood vessel. Embolization is used to treat a wide variety of conditions affecting different organs of the human body. Embolization is commonly used to treat active arterial bleeding.
Why does my child need embolisation?
Your child’s doctor may suggest embolisation for many reasons. If the blood is flowing through a blood vessel too fast, embolisation may be used to slow down the blood flow. Abnormal arteries with abnormal connections to other blood vessels may also benefit from embolisation.
What are the risks of embolization?
Embolization carries many risks. Your likelihood of experiencing them depends on the location of the procedure and type of embolic agent. Potential risks include: Air embolism, when an air bubble blocks a blood vessel. Allergic reaction to contrast dye. Bruising or bleeding at the puncture site. Embolic agent misplacement or migration.
What happens after embolization?
Embolization may also be used to administer chemotherapy. After embolization a tumor may shrink or it may continue to grow but more slowly, making chemotherapy or surgery a more effective option. Eliminate an arteriovenous malformation or arteriovenous fistula (AVF) (abnormal connection or connections between arteries and veins).
What is an embolisation & how does it work?
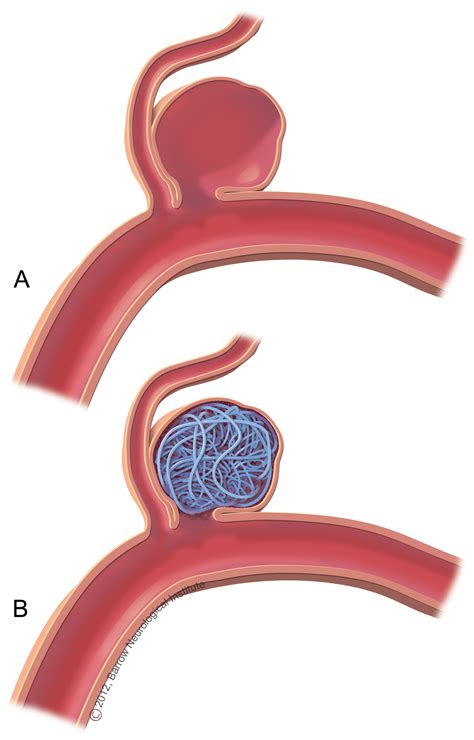
What is an Embolisation? Embolisation is a way of treating ruptured and un-ruptured aneurysms (a balloon like swelling in the wall of an artery) without the need for a Craniotomy (surgical procedure). The neuro-radiologist will approach the aneurysm from inside the blood vessel.
What are the benefits of embolisation?
If the blood is flowing through a blood vessel too fast, embolisation may be used to slow down the blood flow. Abnormal arteries with abnormal connections to other blood vessels may also benefit from embolisation. Embolisation can also be used to shrink abnormal tissue by reducing its blood supply.
What is an example of embolisation?
Usually embolisation is used to block arteries (big vessels carrying blood away from the heart). Very occasionally, embolisation can also be carried out on veins, which carry blood back to the heart. An example of this is Vein of Galen malformation (VGM) – more information is available in a separate information sheet.
embolization References
If you want to know more about embolization, consider exploring links below:
What Is Embolization
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/23512-embolization-procedure
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embolization
- https://www.cvmus.com/vascular-procedures/embolization-procedure-what-expect-and-faq
- https://www.drugs.com/cg/embolization.html
- https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/conditions-and-treatments/procedures-and-treatments/embolisation/
- https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/cathembol
- https://www.uhcw.nhs.uk/download/clientfiles/files/Patient%20Information%20Leaflets/Trauma%20and%20Neuro%20services/Neurosurgery/Embolisation%20A%20Guide%20for%20Patients%20and%20Carers.pdf
- https://www.healthline.com/health/kidney-cancer/embolization-kidney-cancer
- https://www.chelwest.nhs.uk/your-visit/patient-leaflets/imaging/vascular-embolisation
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-42494-1_1
Embolization Information
- https://www.dgft.nhs.uk/leaflet/uterine-artery-embolisation-for-treatment-of-fibroids/
- https://www.nnuh.nhs.uk/publication/download/uterine-artery-embolisation-v7/
- https://www.rcog.org.uk/guidance/browse-all-guidance/other-guidelines-and-reports/uterine-artery-embolisation-in-the-management-of-fibroids/
- https://www.nice.org.uk/Guidance/IPG367
Explore Related Topics
Success Stories: Real-Life Experiences with Varicocele Repair
Engage in conversation by sharing and discussing real-life success stories of individuals who underwent varicocele repair.