Hyperprolactinemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Hyperprolactinemia FAQ
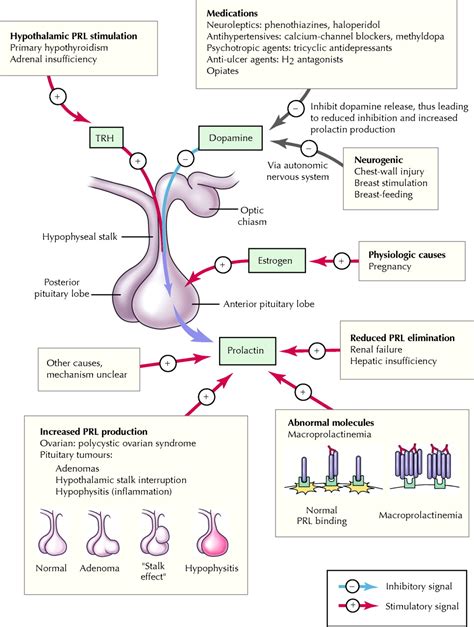
What causes hyperprolactinemia?
Hyperprolactinemia has several causes, including tumors, certain prescription medications, and other health conditions. Tumors. A prolactinoma is a tumor or cancerous growth on the pituitary gland. It is the most common cause of this disease. The tumor produces excess prolactin.
Can a prolactinoma cause hyperprolactinemia?
A prolactinoma is the most common cause of hyperprolactinemia. A prolactinoma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that forms in your pituitary gland and causes excess production of prolactin. In addition to the symptoms of hyperprolactinemia, you may experience the following symptoms if you have a prolactinoma: Headaches. Nausea and/or vomiting.
How is hyperprolactinemia treated?
The treatment for hyperprolactinemia depends on the cause. Some people have high prolactin levels but do not show any symptoms of the condition. They do not need treatment. Options for people who have tumors are: Prescription medicines. Your doctor will prescribe prescription medicines that lower the level of prolactin in the blood.
How do you know if you have hyperprolactinemia?
In some cases, headaches caused by the pituitary tumor or changes in vision may be the first sign of the condition in both men and women. The diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia involves a routine blood test to check prolactin levels. If the levels are elevated, the doctor may want to repeat the test, this time after you fast for at least eight hours.
What does hyperprolactinaemia mean?
Hyperprolactinaemia is the presence of abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. Normal levels average to about 13 ng/mL in women, and 5 ng/mL in men, with an upper normal limit of serum prolactin levels being 15-25 ng/mL for both. When the fasting levels of prolactin in blood exceed this upper limit, hyperprolactinemia is indicated.
What does a high prolactin level mean?
The magnitude that prolactin is elevated can be used as an indicator of the etiology of the hyperprolactinemia diagnosis. Prolactin levels over 250 ng/mL may suggest prolactinoma. Prolactin levels less than 100 ng/mL may suggest drug-induced hyperprolactinemia, macroprolactinemia, nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas, or systemic disorders.
Hyperprolactinemia References
If you want to know more about Hyperprolactinemia, consider exploring links below:
What Is Hyperprolactinemia
- https://www.webmd.com/women/what-is-hyperprolactinemia
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22284-hyperprolactinemia
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-hyperprolactinemia-2616556
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hyperprolactinemia
- https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/hyperprolactinemia
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperprolactinaemia
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537331/
- https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/hyperprolactinemia
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia Information
Explore Related Topics
Personal Experiences with Hormonal Therapy in Male Infertility Treatments
Share your personal stories and testimonials about undergoing hormonal therapy as part of male infertility treatments and inspire a discussion among those who have shared similar experiences.
Are There Age Restrictions or Limitations for Hormonal Therapy in Male Infertility Treatments?
Delve into the topic of age restrictions and limitations related to hormonal therapy for male infertility treatments, and contribute to a discussion on the relevance and significance of age factors.
Hormonal Therapy: A Promising Solution for Male Infertility or Just a Temporary Fix?
Engage in a lively conversation about whether hormonal therapy is a viable long-term solution or merely a temporary fix for male infertility.