Understanding PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder)
PTSD FAQ
What is post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition caused by very stressful, frightening or distressing events. Someone with PTSD often relives the traumatic event through nightmares and flashbacks, and may experience feelings of isolation, irritability and guilt.
What does PTSD feel like?
People with PTSD have intense, disturbing thoughts and feelings related to their experience that last long after the traumatic event has ended. They may relive the event through flashbacks or nightmares; they may feel sadness, fear or anger; and they may feel detached or estranged from other people.
What is complex PTSD?
People who repeatedly experience traumatic situations, such as severe neglect, abuse or violence, may be diagnosed with complex PTSD. Complex PTSD can cause similar symptoms to PTSD and may not develop until years after the event. It's often more severe if the trauma was experienced early in life, as this can affect a child's development.
What does PTSD stand for?
For other uses, see PTSD (disambiguation). Post-traumatic stress disorder ( PTSD) [b] is a mental and behavioral disorder that develops from experiencing a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on a person's life or well-being.
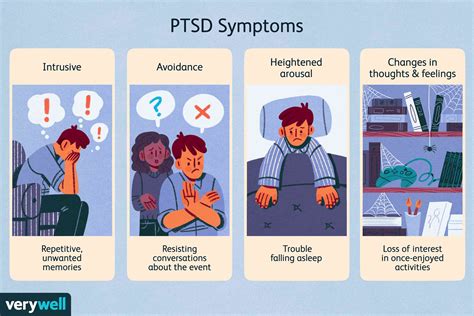
What are the symptoms of PTSD?
Some people with PTSD experience long periods when their symptoms are less noticeable, followed by periods where they get worse. Other people have constant severe symptoms. The specific symptoms of PTSD can vary widely between individuals, but generally fall into the categories described below. Re-experiencing is the most typical symptom of PTSD.
What is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a condition that some people develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic life-threatening event or serious injury. Use the links below to find out more details on what PTSD is, the science of how it affects your brain and body, what types of trauma can cause the condition, and what the symptoms are.
What is PTSD UK?
PTSD UK is the only charity in the UK dedicated to raising awareness of post-traumatic stress disorder – no matter the trauma that caused it. Please help us continue the work we do by donating today (thank you!) What can cause PTSD?
Do you have PTSD after a traumatic event?
After surviving a traumatic event, many people have PTSD-like symptoms at first, such as being unable to stop thinking about what's happened. Fear, anxiety, anger, depression, guilt — all are common reactions to trauma. However, the majority of people exposed to trauma do not develop long-term post-traumatic stress disorder.
PTSD References
If you want to know more about PTSD, consider exploring links below:
What Is PTSD
- https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/conditions/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/overview/
- https://www.mind.org.uk/information-support/types-of-mental-health-problems/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd-and-complex-ptsd/about-ptsd/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/post-traumatic-stress-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20355967
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd
- https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/ptsd/what-is-ptsd
- https://www.rethink.org/advice-and-information/about-mental-illness/learn-more-about-conditions/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/?gad_source=1
- https://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/mental-health/mental-illnesses-and-mental-health-problems/post-traumatic-stress-disorder
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-traumatic_stress_disorder
Explore Related Topics
What Role Does Mental Health Play in Erectile Function?
Engage in a conversation about the connection between mental health and erectile function, sharing tips for managing stress, anxiety, or depression. Encourage users to discuss the impact of mental health on their own erectile function and explore techniques for maintaining good mental well-being.
How Important is Psychological Evaluation Before Opting for Surgery?
Discuss the significance of psychological evaluations as a pre-requisite for undergoing surgical treatments for erectile dysfunction.
Exploring the Influence of Depression on Erectile Dysfunction
Examine the link between depression and erectile dysfunction. Discuss treatment options, support systems, and coping strategies for individuals experiencing both conditions.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy vs. Psychotherapy: Which is more Effective for Treating Mood Disorders?
Compare the effectiveness of testosterone replacement therapy and psychotherapy as treatments for mood disorders in men.